The term weather is used for short-term atmospheric conditions. The data of weather comes from the metrological departments. Long-term weather conditions are termed as climate. Earlier, the term ‘global warming’ was commonly used for long-term change of weather conditions, which is even interchangeably used for climate change at present. The most trusted and well accepted data for climate change comes from Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), established by World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). Majority of the environmental scientists believe that climate change is a manmade change due to greenhouse gas emissions, especially carbon dioxide. It is established that there was a hot period during the midlevel age and then there was a cold period during the ice age and similar cycles have been believed to exist for million years ago too. At present, there are no disagreements of scientists, politicians and civil society on the rise of global average temperatures and their contribution in the rise in number and intensity of natural disasters.
When we blame humans for the climate change, this needs scientific logics and mechanisms to accept or reject the belief. To understand the global warming, it is necessary to bring in the knowledge of heat energy and material balances to comment on the aspect. When we talk of heat energy for global warming, we generally refer to Sun’s heat energy. Whereas, material balance refers to the balance of water of earth system and more importantly the gases that contribute to the global warming.
The Sun’s energy heats up the Earth and the procedure is called the greenhouse effect. Without greenhouse effect, temperature of Earth will fall to minus eighteen degrees centigrade, which is an unbearable temperature and no humans might have existed on such a cold scale. In the natural greenhouse effect, some of the heat is trapped by the Earth and remaining is returned. Water vapors, Carbon dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), Nitrous oxide (N2O), Ozone (O3), Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), Hydrofluorocarbons (HCFCs and HFCs) are the major greenhouse gases. The weather or climate is governed by five key parameters air and ocean temperature, air pressure, air velocity, air density and moisture. Dr. Christopher Budd, a Professor of Applied Mathematics at the University of Bath, and Professor of Geometry at Gresham College UK explains that climate parameters are affected by solar radiation, Earth’s rotation, Gravity, mountains, vegetation, ice and greenhouse gases. An energy balance of Sun shows that if we subtract the energy which is absorbed by the Earth shall give the energy, which is reflected as short wavelength or ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Percentage of reflection of UV radiations in science is called Albedo. Higher the Albedo, higher will be the reflection of heat, which will lead to the lower absorbance of heat hence lower global warming. Albedo is measured in fraction, the lowest being 0 the highest 1. Earlier means no reflection of heat radiations at all, whereas latter means reflection of all heat.
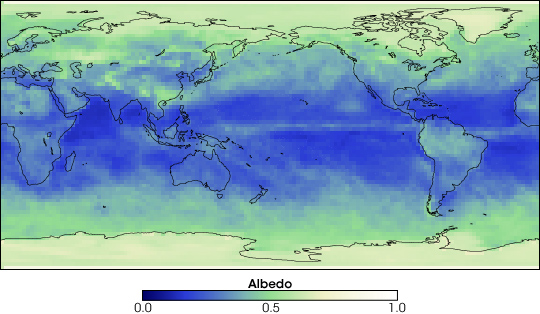
The heat radiations that come from Sun are of short wavelength. When these radiations strike the Earth, they re-reflect to space as long weave length, scientifically called infra-red radiations. The amount of the radiation, which is reflected as heat radiations follow the blackbody radiation law proposed by Max Planck, a famous German Physicist. The law is also called Planck’s Law of blackbody radiation. A blackbody is “a hypothetical perfect absorber and radiator of energy, with no reflecting power.” As per blackbody radiation law, “the radiation is proportional to the fourth power of the absolute Temperature.” A more generic mathematical relation shows that the average global temperature increases with decrease in each Albedo and emissivity. “The emissivity of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in emitting energy as thermal radiation.” A perfect blackbody will have the lowest possible Albedo reaching to 0, whereas white body, which is opposite to a blackbody will have the highest value of Albedo approaching to 1.
Earth is not a perfect blackbody hence; it partially absorbs and radiates the heat energy. The radiations that return to space as long wavelength, which get absorbed in the blanket of greenhouse gases. As the concentration of greenhouse gases increase, blanket thickens which in result lowers the emissivity of the atmosphere. For example, the emissivity of carbon dioxide at 200 parts per million (ppm) is 0.194, at 400 ppm is 0.14, and at 800 is 0.085. Earth’s average Albedo is 0.3. It depends upon the planet’s physical characteristics and vary from location to location depending upon the medium present. The lowest Albedo of 0.03 is for water and the highest is for ice-sheets, which is up to 0.95. This means water can absorb almost 97% of heat, whereas ice-sheets can only absorb as low as 5%. It is reported that the Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) measured an albedo decrease of 0.0027 from 2000 through 2004. Recent studies on Arctic has shown decline in its albedo as well.
Lowering the emissivity of heat radiations of atmosphere due to increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide is one of the vivid scientific evidences to accept that manmade greenhouses, specially carbon dioxide emissions are one of major reasons for climate change. As ice-sheets are melting rapidly, this further enlightens the scientific evidence that the average Albedo of Earth is decreasing. Temperature, emissivity, albedo and densities of greenhouse gases are interconnected, and their interchanging effects are catalytic. Temperature, emissivity and albedos cannot be controlled or altered artificially at global level. However, emissions of greenhouses gases can be controlled and reduced which seems to be the way forward to avoid a climatic catastrophe.
